Hydrogen Microgrids: The Game Changer for Resilient, Emission-Free Hospitals
When Hurricane Sandy knocked out power to Lower Manhattan in 2012, NYU Langone Medical Center had to evacuate 300 patients, including babies from the NICU, down darkened stairwells. It's a scenario no hospital administrator ever wants to face, yet it highlights a critical vulnerability in our healthcare infrastructure: the complete dependence on an aging electrical grid.
Traditional backup generators have been the go-to solution for decades, but they're far from perfect. They're loud, they pollute, they require constant fuel deliveries, and honestly? They fail when you need them most. That's where hydrogen microgrids are stepping up as the real game-changer for hospitals that need both bulletproof reliability and clean energy.
Why Hospitals Are Different Energy Animals
Let's get one thing straight, hospitals aren't your typical buildings. They consume about 2.5 times more energy per square foot than regular commercial spaces, and they never, ever get to take a break. Life support machines, surgical equipment, refrigeration for medications, HVAC systems maintaining sterile environments, it all has to run 24/7, no exceptions.

When the power goes out, hospitals have minutes (sometimes seconds) before critical systems start failing. Traditional diesel generators can kick in, sure, but they come with a whole host of problems. They're noisy in environments where patients need peace to heal. They pump out emissions that can be dangerous to people with compromised respiratory systems. And during extended outages or natural disasters, getting fuel deliveries becomes a nightmare.
We've seen this play out repeatedly. During Hurricane Katrina, multiple hospitals lost power for days. During the Texas freeze in 2021, hospitals struggled to maintain operations as the grid failed. Each time, it becomes painfully clear that our current backup systems aren't cutting it.
Enter Hydrogen Microgrids: The Clean Energy Cavalry
So what exactly is a hydrogen microgrid, and why should hospital administrators care? Think of it as a sophisticated, self-contained power network that can operate independently from the main electrical grid. Instead of relying on diesel generators, these systems use hydrogen fuel cells as their primary backup power source.
The beauty of hydrogen fuel cells is in their simplicity and reliability. They combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, with the only byproduct being water vapor. No combustion, no emissions, no noise, just clean, reliable power that can run as long as you have hydrogen supply.
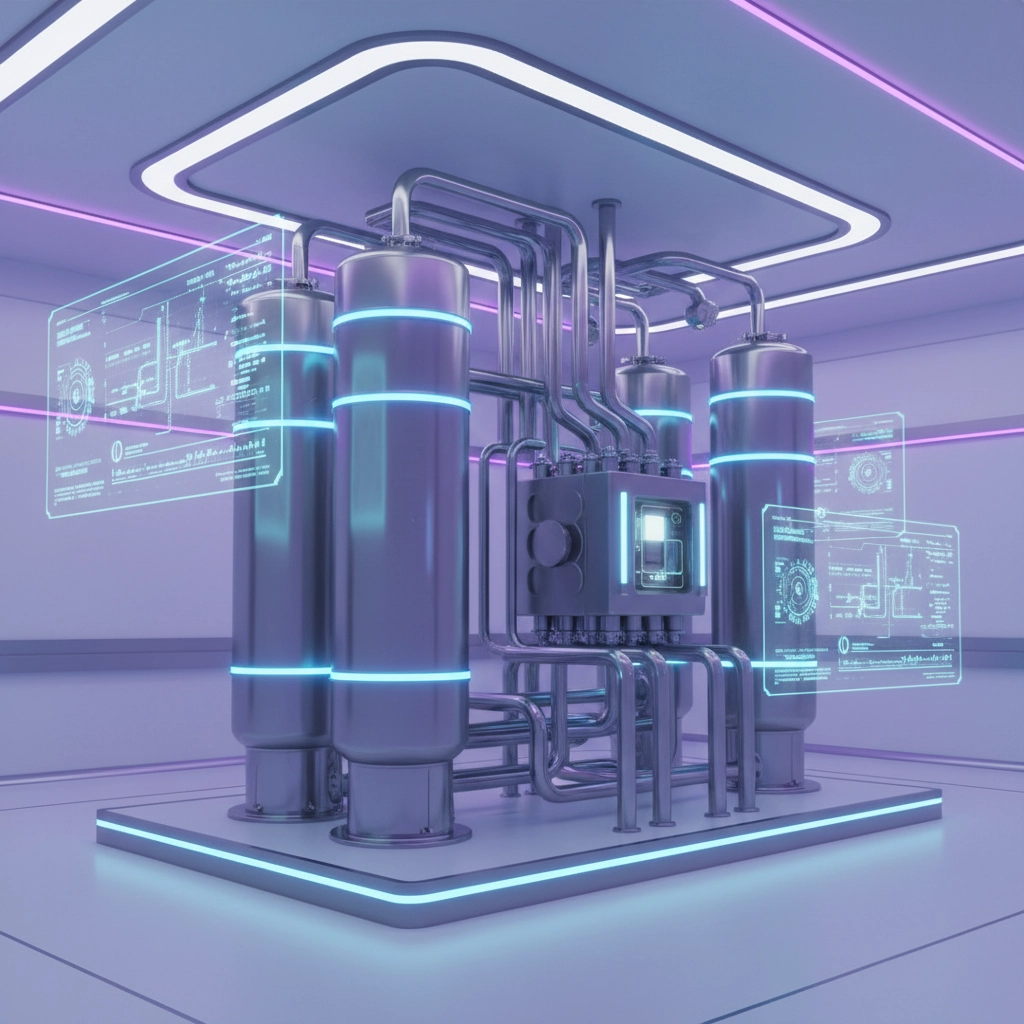

These systems typically include multiple components working together: hydrogen fuel cells for primary backup power, battery storage for immediate response to power fluctuations, smart controls that manage energy flow and automatically switch between grid and backup power, and often renewable energy sources like solar panels that can produce green hydrogen on-site.
The real magic happens in how these components work together. When the grid is stable, the system operates in "grid-connected" mode, potentially even selling excess power back to the utility. But when there's an outage, it seamlessly switches to "island mode," providing uninterrupted power for as long as needed.
Resilience That Actually Works
Here's where hydrogen microgrids really shine compared to traditional backup systems. Diesel generators are great for short-term outages, but they're not designed for extended operations. They need regular fuel deliveries, they require maintenance that can be challenging during disasters, and they have mechanical parts that can fail.
Hydrogen fuel cells, on the other hand, can operate continuously for weeks or even months with proper hydrogen supply. They have fewer moving parts, which means fewer failure points. And unlike generators that might struggle to start in extreme weather conditions, fuel cells operate reliably across a wide temperature range.
The University of California, Irvine, has been pioneering this technology with their hydrogen microgrid that serves critical facilities on campus. During planned grid maintenance and unexpected outages, their system has provided seamless backup power, proving that the technology isn't just theoretical, it works in the real world.
But resilience isn't just about having backup power, it's about having reliable backup power. Traditional systems often force hospitals to operate in "emergency mode" during outages, limiting services to only the most critical functions. With hydrogen microgrids providing full power capacity, hospitals can maintain normal operations, continue elective procedures, and keep all patient care areas fully functional.
Zero Emissions: Clean Air for Healing
Let's talk about something that should matter to every healthcare facility: air quality. Hospitals treat patients with respiratory conditions, immune system compromises, and other health issues that make them particularly vulnerable to air pollution. Yet many hospitals are still using backup generators that pump diesel fumes directly into the surrounding air.
This isn't just an environmental issue, it's a patient safety issue. The American Hospital Association has noted that emissions from backup generators can pose health risks to vulnerable populations, which is basically describing every hospital patient.
Hydrogen fuel cells eliminate this problem entirely. When using green hydrogen (produced from renewable energy sources), the entire process is emission-free. Solar or wind power electrolyzes water to create hydrogen, which is then stored and used in fuel cells that produce only electricity and water vapor. It's a completely clean cycle that aligns with healthcare's mission of "first, do no harm."

Some forward-thinking hospitals are already making this connection. Kaiser Permanente, for example, has been investing heavily in renewable energy and clean backup power solutions as part of their commitment to environmental health. They recognize that a hospital's environmental impact isn't separate from their healthcare mission, it's part of it.
The Economics Make Sense
Now, let's address the elephant in the room: cost. Yes, hydrogen microgrids require a significant upfront investment. But the economics are more favorable than you might think, especially when you factor in the total cost of ownership over time.
Traditional generator systems seem cheaper initially, but they come with ongoing costs that add up quickly. Fuel costs, regular maintenance, testing requirements, emissions compliance, and periodic replacement all chip away at the budget year after year. Diesel fuel prices can be volatile, and during emergencies, fuel costs can skyrocket.
Hydrogen microgrids flip this equation. While the initial capital investment is higher, operational costs are typically lower and more predictable. Fuel cells require less maintenance than combustion generators, they last longer, and if you're producing your own green hydrogen on-site, you're insulated from fuel price volatility.
Plus, these systems can generate revenue when they're not needed for backup power. Hospitals can participate in grid services, selling excess power during peak demand periods when electricity prices are highest. Some systems can even provide grid stabilization services, creating additional revenue streams.
The Massachusetts General Hospital Brigham Integrated Care System has been exploring these economic benefits, finding that their microgrid investments not only improve resilience but also contribute to long-term cost savings through energy optimization and demand management.
Real-World Success Stories
The technology isn't just theoretical anymore: it's being deployed and proven in real healthcare settings. In California, several medical facilities have implemented hydrogen fuel cell systems as part of their resilience planning. These installations have successfully provided backup power during planned outages and emergency situations, demonstrating the reliability healthcare facilities need.
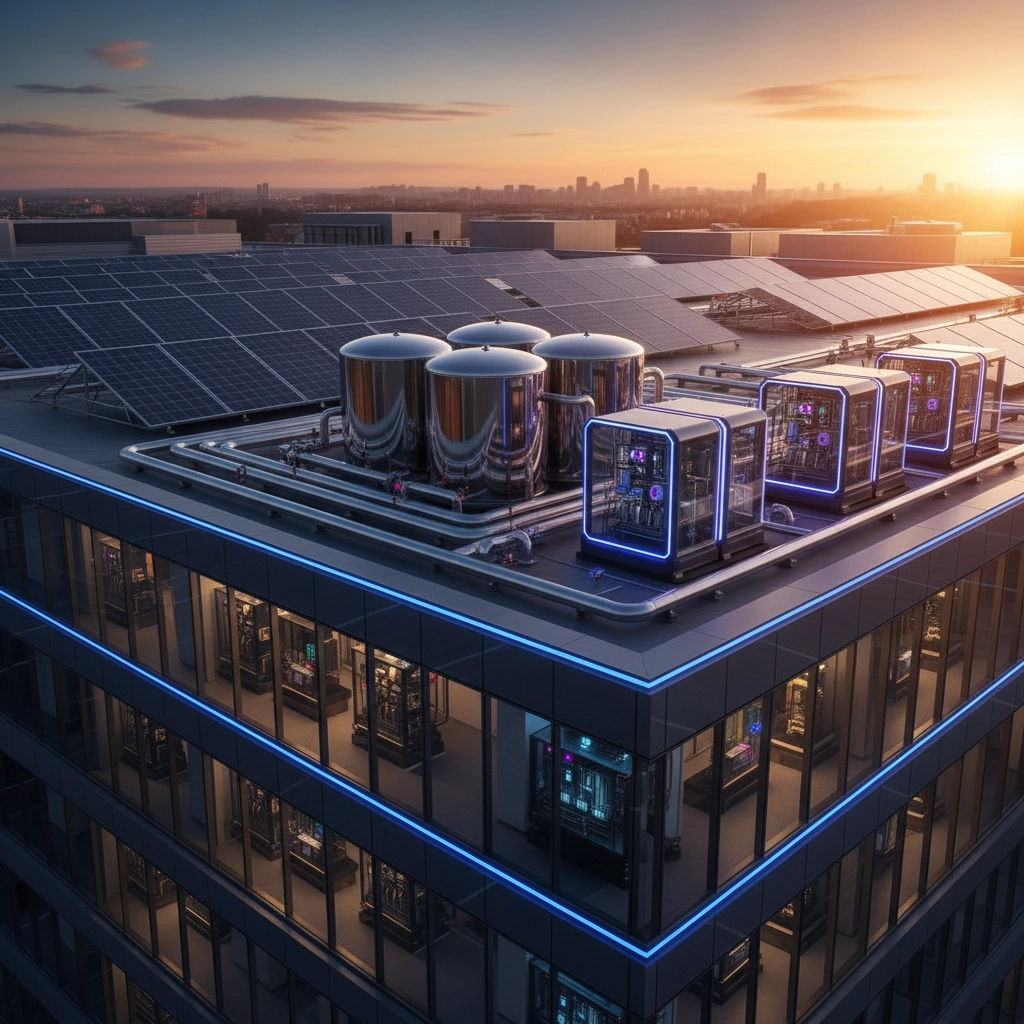

One particularly compelling example is the growing trend of "resilience hubs": community facilities that can serve as safe havens during extended power outages. Hospitals are natural candidates for these hubs, and hydrogen microgrids enable them to not only maintain their own operations but also provide critical services to the broader community during disasters.
In South Korea, hydrogen fuel cell systems are being integrated into smart city infrastructure, including healthcare facilities. These projects are providing valuable real-world data on system performance, maintenance requirements, and integration with existing hospital infrastructure.
The Path Forward
As we look toward the future, hydrogen microgrids represent more than just a backup power solution: they're a pathway to energy independence for critical facilities. The technology continues to improve rapidly, with costs declining and efficiency increasing. More importantly, the supporting infrastructure is developing, with hydrogen production, storage, and distribution becoming more accessible.
For hospital administrators considering their energy future, the question isn't whether to invest in resilience: it's which solution provides the best combination of reliability, sustainability, and economic value. Hydrogen microgrids are emerging as the clear answer for facilities that refuse to compromise on any of these factors.
The healthcare sector has always been about saving lives. Now, with hydrogen microgrids, hospitals can save lives while also protecting the environment that all our lives depend on. That's not just smart business: it's the kind of pioneering thinking that moves entire industries forward.
Ready to explore how hydrogen solutions could transform your facility's energy resilience? Visit our hydrogen energy solutions page to learn more about the technologies that are reshaping critical infrastructure across the country.







